Helminths are subcutaneous parasites that live in the human body. They feed on the cells of the host, releasing toxic substances. Infection with parasites can lead to serious illness, in the worst case to death. Depending on the type of worms, their locations vary. Some multiply in organs, others live under human skin, provoking the development of dermatoses.
Varieties of subcutaneous parasites and methods of infection
Parasitic skin diseases are not common types of pathologies. However, cases of the disease have been reported. Most likely they are after visiting Asian regions and countries with hot climates. Parasites in the human body provoke an allergic reaction, accompanied by unbearable itching.
In medicine, worms are divided into two types:
- Subcutaneously. Helminths are difficult to diagnose. After infection and the maturation stage, the parasites move through the human body. The most common types of subcutaneous helminths are: iron, scabies, filariasis, scabies.
- Dermal. After contact with human skin, the parasites migrate to different parts of the body. Inflammation of the pancreas, development of scaly lichens, eczematosis and diabetes mellitus occur as a result of infection with skin parasites.
Common cases include a tick infection localized in the sebaceous glands. It is characterized by an exit to the surface of the epidermis during the day for the supply of secretions from the skin canals.
Filariasis
Filariasis is the defeat of a person by parasites of the nematode type. It is found in the countries of the Asian region, as well as in places with tropical climates. The most likely way of infection is when visiting resort areas. The main danger from parasites is the long incubation period. Without symptoms, worms can live under the skin for 5 to 7 years. Pests are characterized by excessive vital activity, which provokes symptoms of intoxication in the patient.
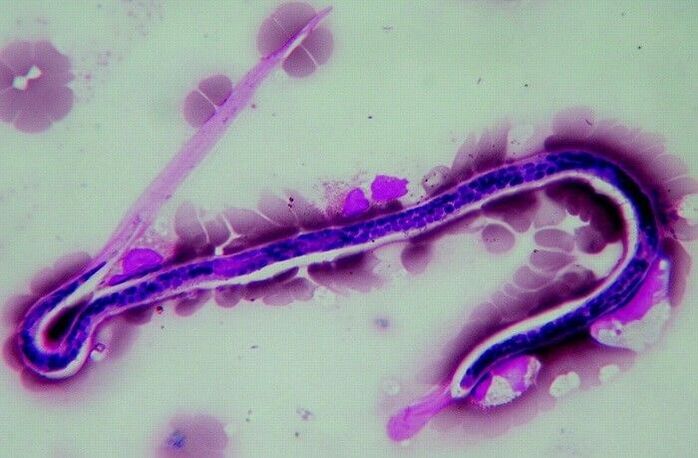
In the early stages of the disease there are signs of urticaria. As worms grow and multiply, there is loss of vision, formation of removable seals and fever. In the later stages, the location of the worms is determined with the naked eye.
Dracunculiasis
Dracunculiasis is a disease caused by a subcutaneous helminth infection. They can live in open water. Human invasion occurs during travel when drinking raw water from untested sources. In an infected person, the larvae are located below the upper layer of the epidermis. The presence of even one parasite without proper treatment leads to death. Adult helminths with a length of 100 centimeters have been registered in the world practice. They are able to occupy the entire space of the stomach, liver or block the airways. Most often, helminths are localized in the lower extremities of a person.
Most often, helminths are localized in the lower extremities of a person.
The main symptoms of a lesion include:
- rashes on the legs;
- the formation of fluid-filled blisters;
- unbearable itching;
- the appearance of bumps;
- purulent formations.
The main treatment is surgical removal of the helminth from the body.
schistosomiasis
The disease provokes a number of types of helminths that are found in water bodies. Infection occurs when swimming in rivers and lakes of the African and Asian regions. Another way of infection is untested drinking water. It is a source of spread of eggs and larvae of parasites. Initially, helminths are localized under the epidermis. An allergic rash forms on the skin, accompanied by itching. As the disease progresses, the larvae penetrate deep into the body. The patient's kidneys and liver are severely affected. The disease is accompanied by night fever, profuse sweating. Enlarged liver and deformed kidneys can help diagnose infection.
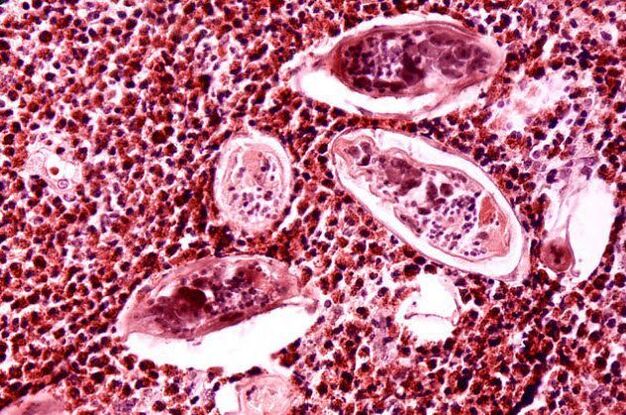
Cysticercosis
Cysticercosis is a disease associated with human infection with swine tapeworm. The parasite belongs to the category of stubborn, lives in Asian countries. For the development of an adult in the human body is sufficient penetration of 1 larva or part of a worm. The parasites are highly regenerative, which complicates the healing process.
The main signs of damage include urticaria, itching, general weakness, pain. Often worms are localized under the skin, in the muscles, eyes, internal organs and brain. During adult development, a tubercle or seal forms under the skin. Over time, it can increase, this brings inconvenience. The main breeding grounds for swine tapeworm are the shoulders, chest, arms, palms.
Heartworm disease
The main method of infecting with worms is the penetration of larvae through insect bites or contact with animals. Temporary carriers of larvae are cats and dogs, mosquitoes act as carriers. The female worm is 30 centimeters long, the male 10 centimeters.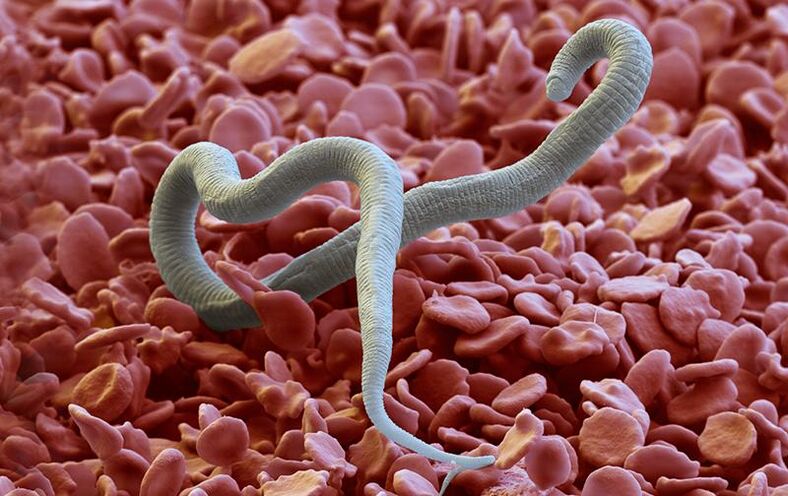 The development of parasites occurs under the upper layer of the epidermis.
The development of parasites occurs under the upper layer of the epidermis.
The eggs remain on human skin when bitten by a mosquito. The hatched larva penetrates deep into the skin through the injured area of skin. There she goes through all the stages of growth. The disease is accompanied by unbearable itching. Seals are noted in the areas of worm localization. The patient feels the movement of adults under the skin. Vision loss is possible if it is affected by helminths.
The treatment of worms is performed surgically. After the operation, patients are shown drugs that repair the skin and affected organs.
Scabies
Scabies is an infection of a person with scabies mites. The disease gets its name because of the strong, unbearable itching all over the body. In places where ticks are localized, people develop redness and spots.
Infection with ticks occurs through physical contact with an infected person or his personal belongings. The diagnosis is made by visual examination of the skin and laboratory tests.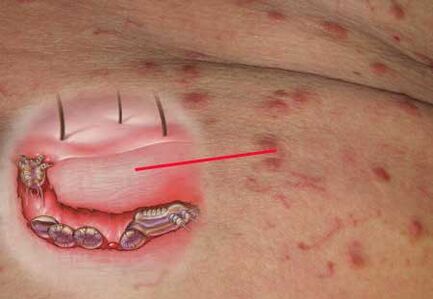 Iodine diagnosis can be done at home. When it comes in contact with the affected skin, a cobweb is seen - the path of movement of ticks under the skin of an infected person.
Iodine diagnosis can be done at home. When it comes in contact with the affected skin, a cobweb is seen - the path of movement of ticks under the skin of an infected person.
The main symptoms of scabies include:
- itching and redness of the skin;
- the formation of fluid-filled blisters when scratching the skin;
- localization of lesions on the hands and joints.
The treatment of the disease is long and laborious. It is almost impossible to completely eliminate parasites.
demodicosis
Demodectic mange is a human infection with subcutaneous ticks. They are localized in the sebaceous glands of the infected. In the early stages, the disease can easily be confused with acne. As the mites multiply, the rash increases and spreads throughout the face. Eyelash loss begins.
The diagnosis of demodicosis is simple. For this purpose, a visual inspection is performed and a number of laboratory tests are performed. The treatment of the disease is long-term. In some cases, this takes several years. Infection with ticks occurs through direct contact with the patient, the use of personal belongings or cosmetics of the infected. Successful reproduction of ticks is facilitated by an unstable hormonal background, weakened immune system.
Symptoms of the disease
Modern medicine distinguishes several types of subcutaneous parasites. They provoke the development of skin dermatitis and dysfunction of internal organs. Depending on the pathogen in humans, the symptoms manifest in a special way. However, there are a number of signs, when they appear, it is recommended to consult a specialist.
You can learn about worms in the body by a number of signs:
- general weakness;
- raising the temperature to 39 ° C;
- itchy skin of varying intensity;
- the appearance of skin rashes;
- upset gastrointestinal tract;
- the formation of seals on the skin.
It is important to note that an early visit to the doctor allows you to quickly rid the body of parasites living under human skin.
Diagnostic characteristics
Subcutaneous parasites in humans are difficult to diagnose. For this reason, at the first suspicion of a lesion it is necessary to consult a specialist. The complexity of the diagnosis is directly related to the latent course of the disease. In general, bright symptoms appear only a few years after the lesion, which adversely affects health.

A number of symptoms indicate helminth infestation, but there is no general clinical picture of manifestation. It is necessary to exclude the defeat of the patient with helminths in case of reddening of the skin, the appearance of constant itching, various seals on the skin.
A visit to a number of specialists allows you to make the correct diagnosis:
- dermatologist;
- neurologist;
- allergist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- psychologist.
The consultation with a psychologist is carried out if no deviations in the direction of other specialists are found.
To clarify the diagnosis of patients, laboratory tests are ordered:
- blood test for antigens;
- examination of a skin sample;
- smear;
- secret research;
- scraping from the affected area.
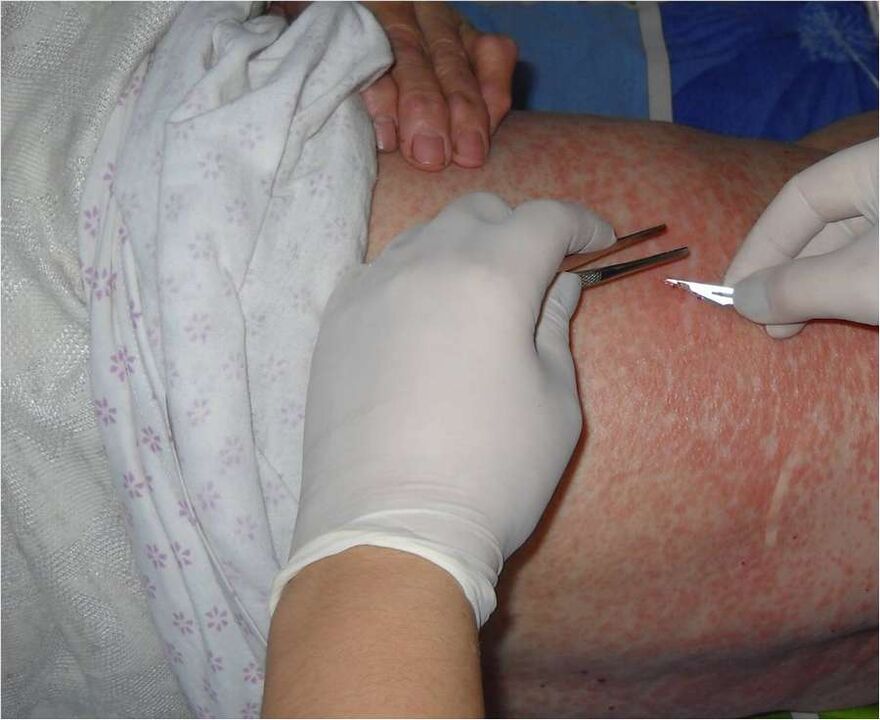
The results of laboratory tests can detect parasites under the skin. If in the last six months before the onset of symptoms there have been trips to Asian countries or other tropical regions, this fact should be reported to the doctor.
Diagnosis of subcutaneous parasites requires the appointment of a competent therapeutic regimen. In this situation, the use of drugs or methods of traditional medicine that are not recommended by the attending physician is prohibited. Violation of the therapeutic regimen can lead to deterioration and poisoning of the body.
Effective treatments
In medical practice there are two methods of treating parasites: medical and surgical. Depending on the complexity of the lesion, the doctor uses one method or both in combination. The choice of therapeutic methods of treatment depends on the risk to the patient's health and the characteristics of the parasites.
The choice of treatment method is influenced by:
- the number of parasites in the patient's body;
- regenerative ability of the worm;
- playback speed;
- localization of parasites;
- allergic reactions of the patient;
- the severity of the disease;
- possible or existing complications.
Drug treatment involves taking a course of medication. The action of drugs involves exposure in several directions:
- Destruction of adult worms and larvae in the body, preventing their reproduction. Anthelmintic drugs are used for this.
- Eliminate inflammation and destroy outbreaks of infection. For this, a course of antibiotic therapy is conducted.
- Accelerate the elimination of toxins and eliminate allergic reactions. The patient is prescribed a course of antihistamines and glucocorticoids.
- Healing of the affected areas of the skin. Creams and ointments are used to accelerate the regenerative function of the epidermis.
Surgical treatment of subcutaneous parasites is recommended in cases where there are serious complications and there is a special location of the worm. The operation has shown high efficiency in cases where it is known that the body is affected by only one individual. Surgery is most often used for dracunculiasis. The worm's internal fluid contains toxic substances that can cause anaphylactic shock. In this case, complete extraction of the parasite is shown.
Methods of prevention
Infection with skin parasites in humans requires long-term therapy. The problem can be avoided by following a number of preventive measures:
- Observance of the rules of hygiene. Hands should be washed under running water with soap or antiseptic. Especially after contact with unknown or stray animals. Scratches, cuts and other damage to the skin should be treated with antiseptic.
- Food processing. Fresh vegetables and fruits should be rinsed thoroughly under running water before use. Heating of fish, poultry and meat is recommended. Avoid eating raw or semi-raw meat.
- Use of proven water sources. Water from unknown sources should be treated. Outdoor pools and springs deserve special attention.
- Routine vaccination. Before traveling to tropical countries, it is necessary to be vaccinated against major diseases.
- General use of makeup. Women should avoid sharing makeup, even with close friends.
- Swimming in open waters. Swimming in polluted or untested water pools is prohibited. During the hot season, preference should be given to water bodies that have been tested for water quality.
Responsible attitude to one's own health and observance of preventive measures helps to prevent parasitic skin diseases.